Publication 01
Journal: Coal Journal
Paper Title: Control Measures of Freezing Reinforcement and Freezing Expansion for Metro Two-Line Tunnel Passing Under Existing Stations (2024)
Authors:Chen Xiangsheng, Ding Hang, Li Fangzheng, Chen Xi, Gao Wei, Wang Heng, Wang Lei, Chen Hanqing
INTRODUCTION: During the freezing construction period, the water in the ground expands in volume after freezing, resulting in the freezing and expansion effect. This phenomenon causes serious squeezing on underground structures, adjacent pipelines, and surface buildings (structures), and even leads to damage. In long-distance and large cross-section underground projects such as subway stations and tunnels crossing obstacles, the volume of frozen soil formed during the construction using the freezing method is dozens of times more than that of the conventional subway liaison channel freezing project, and its freezing and expansion effect is even more significant. Therefore, how to effectively control the freezing effect in this kind of project is a technical problem that needs to be solved in freezing construction. At present, there is still a lack of in-depth research on the evolution law and control technology of freezing and deformation in urban long-distance and large cross-section underground freezing projects.
In this study, the freezing project of Shanghai Metro Line 18 under Guoquan Road Station is taken as the background, and the influence laws of measures such as staggered freezing and brine temperature regulation on the freezing deformation are investigated through the establishment of a three-dimensional refined thermal coupling model. Freezing control measures based on temporal and spatial effects are proposed to effectively control the frozen soil volume and boundary in both time and space dimensions, and the effectiveness of the control measures is verified by field data. The research results provide guidance for the freeze-up control technology of urban long-distance and large-section underground space freezing project.

Main innovation points:
1. Revealed the evolution law of freeze-distortion displacement field under staggered freezing mode
Adopting the staggered freezing mode can prolong the time point when the freezing and expansion deformation reaches the peak value, and avoid the superposition of the freezing and expansion effects in the same time period. In the engineering design stage, the proposed freezing area can be divided into a number of freezing batches through the method of “layering, zoning, and sequencing” to implement progressive active freezing, which can reduce the influence of freezing and expansion effects on the neighboring structures in the same period of time. In the process of active freezing, auxiliary measures such as soil extraction and pressure relief can also be combined to reduce the adverse effects of frost heave.
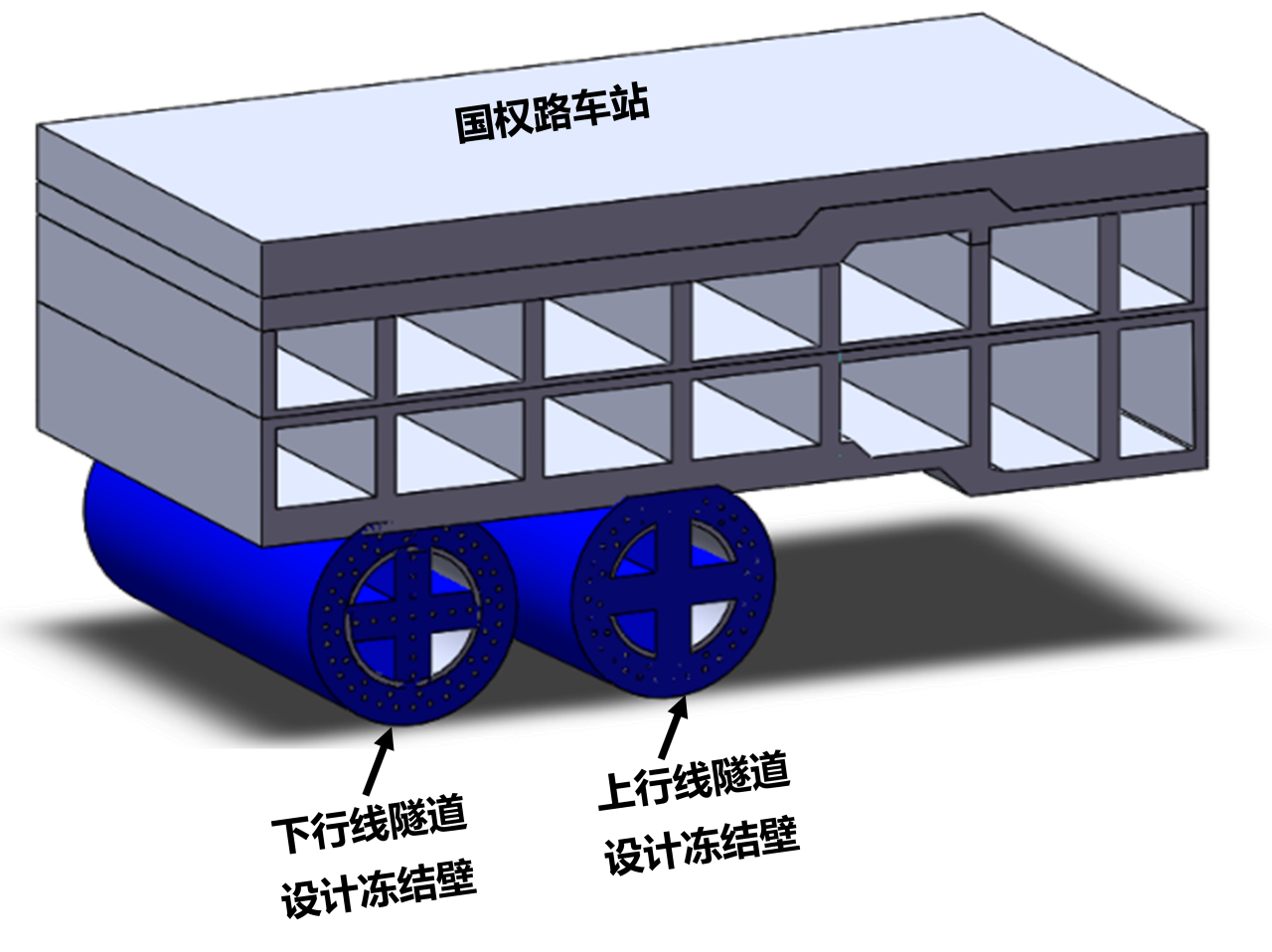
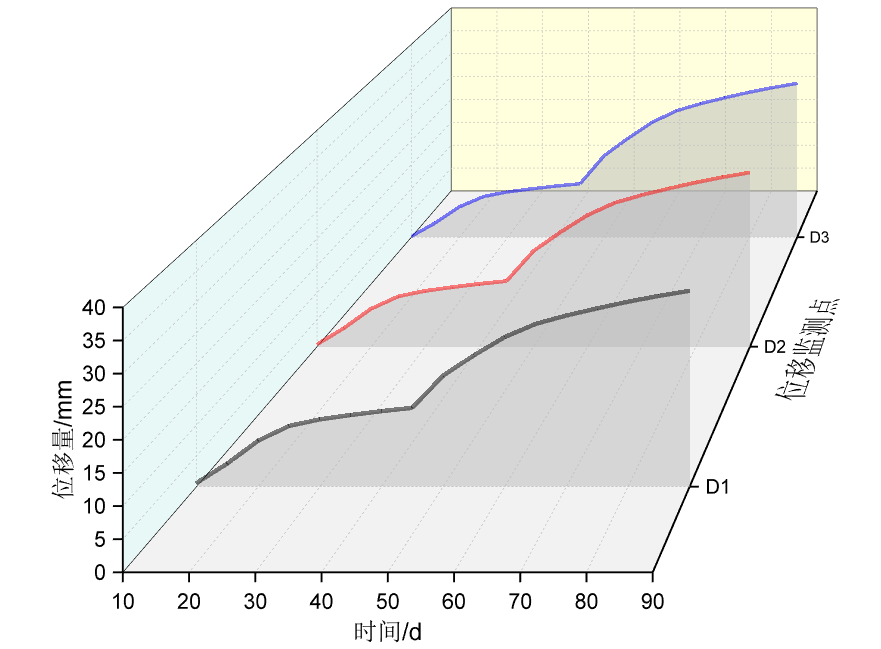
2. Freezing and expansion control measures based on spatio-temporal effects are proposed
For the urban long-distance horizontal freezing and clearing project, freezing and expansion control measures based on spatio-temporal effects are proposed. In the time dimension, through the staggered freezing mode, the volume of frozen soil in a single stage is accurately regulated to avoid the spatial and temporal accumulation of the superposition effect of freezing and expansion; in the spatial dimension, based on the thermodynamic coupling mechanism of frozen soil, the development rate of the freezing wall and the boundary morphology of the frozen wall is finely controlled through the control of the brine temperature and other measures, so as to effectively reduce the effect of the freezing and expansion effect on the surrounding environment.


Publication 02
Journal: Coal Science and Technology
Thesis title: Current status and development trend of mechanized digging of frozen vertical shafts (2024)
Authors:Chen Xiangsheng, Wang Heng, Song Chaoyang, Chen Hanqing, Chen Xi, Ding Hang, Wang Lei
Introduction:Drilling and blasting method of shaft drilling is the main method of vertical wellbore construction in China, the application of explosives improves the drilling efficiency of frozen wellbore, and the application of large-scale mechanized equipments, such as umbrella drill drilling, rock grabbing machine loading, large derrick and equipment lifting, and large formwork wall laying, improves the speed of wellbore formation; vertical drilling rigs, backhoe drilling rigs, and vertical shaft drilling rigs as the special drilling methods of vertical wellbore under special stratigraphical condition also have their own scope of application. their own scope of application.
Facing the characteristics of water-rich and weakly cemented strata and the development trend of intelligent mine in western China, it is difficult to meet the demand for intelligent and unmanned construction of vertical wellbore in kilometer-scale weakly cemented rock formation by freezing + drilling and blasting method, and the use of freezing + shaft boring machine drilling will be one of the directions of the future development of ultra-deep vertical wellbore technology. Combined with foreign engineering cases, rationalization suggestions are put forward for the construction of vertical wellbore in water-rich and weakly cemented rock formations in western China in terms offreezing-excavating-supporting-transporting coordinated operation; the interaction mechanism between the well wall structure and the weakly cemented surrounding rock is revealed, the method of double-wall structure is optimized, and the synchronous operation mode of vertical shaft boring machine excavating-supporting-transporting is constructed, and so on. -The method of double-layer wall structure is optimized, and the synchronous operation mode of vertical shaft digging machine for digging, supporting and transporting is constructed, which improves the comprehensive efficiency of shaft construction and the level of informationization, and promotes the development of vertical shafts towards mechanization, greening and intelligence.

Main innovation points:
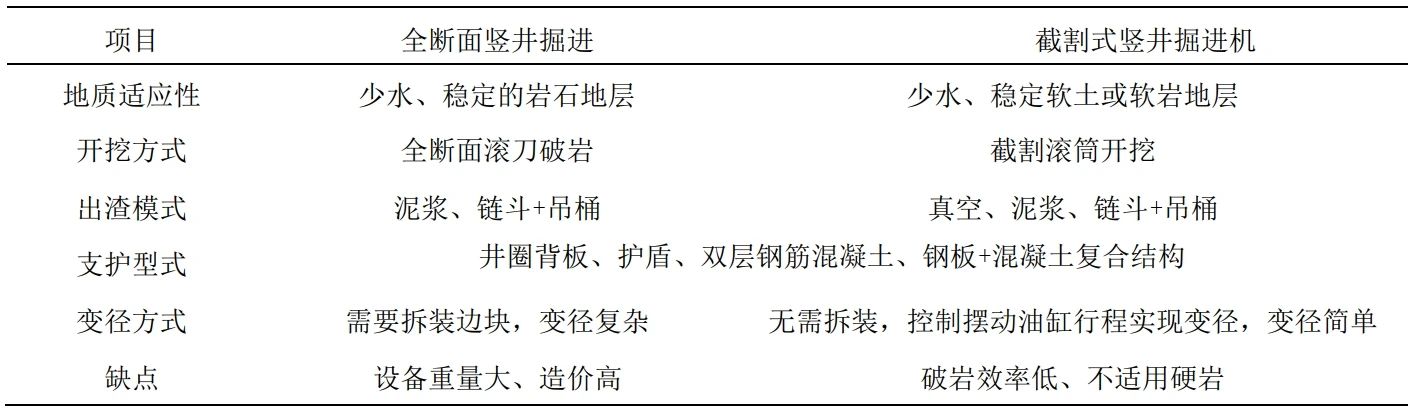
1, summarized the characteristics of freezing method and mechanical method of excavation and construction of vertical wells in China
Discusses the origin, development and evolution of freezing wall and freezing well wall in China, analyzes the current status of mechanized construction under the condition of weakly cemented rock formation in the typical western part of China, and clarifies the two main features of the large thickness of the well wall and the restriction of the construction of the drilling and blasting method, which require the use of new mechanical rock-breaking methods for the freezing of the vertical shaft excavation and masonry construction.
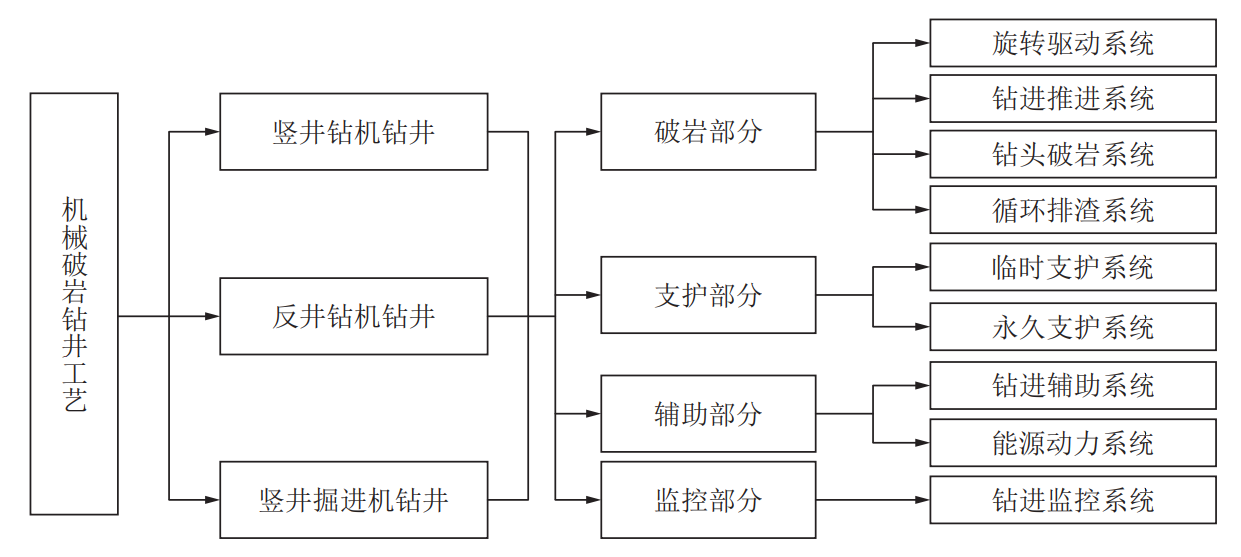
2、Proposed a design idea of freezing well wall for weakly cemented rock formations in the west.
The freezing wall of deep vertical wells usually adopts high-performance concrete and high reinforcement rate to improve the strength of the wall and realize the thinning of the wall. However, this method neglects the form of interaction between the wall structure and the surrounding rock and the load transfer mode, which makes it difficult to reveal the stress mechanism of the wall structure. In view of this, based on the freezing design theory, the two-way adjustment of well wall material and load is realized by adjusting the design parameters of the well wall structure, and a reasonable calculation method of the well wall is finally determined.
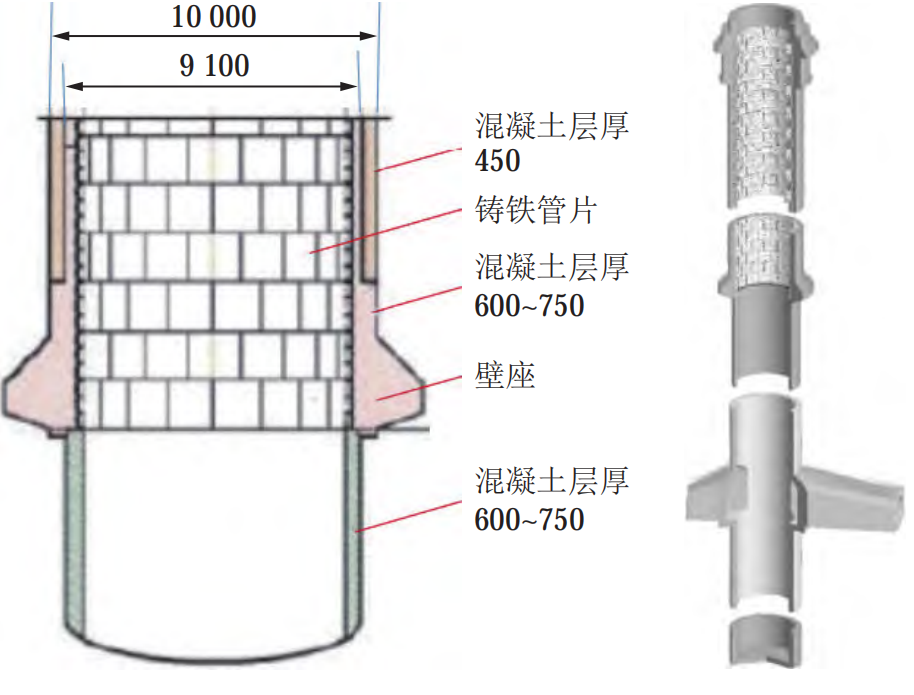
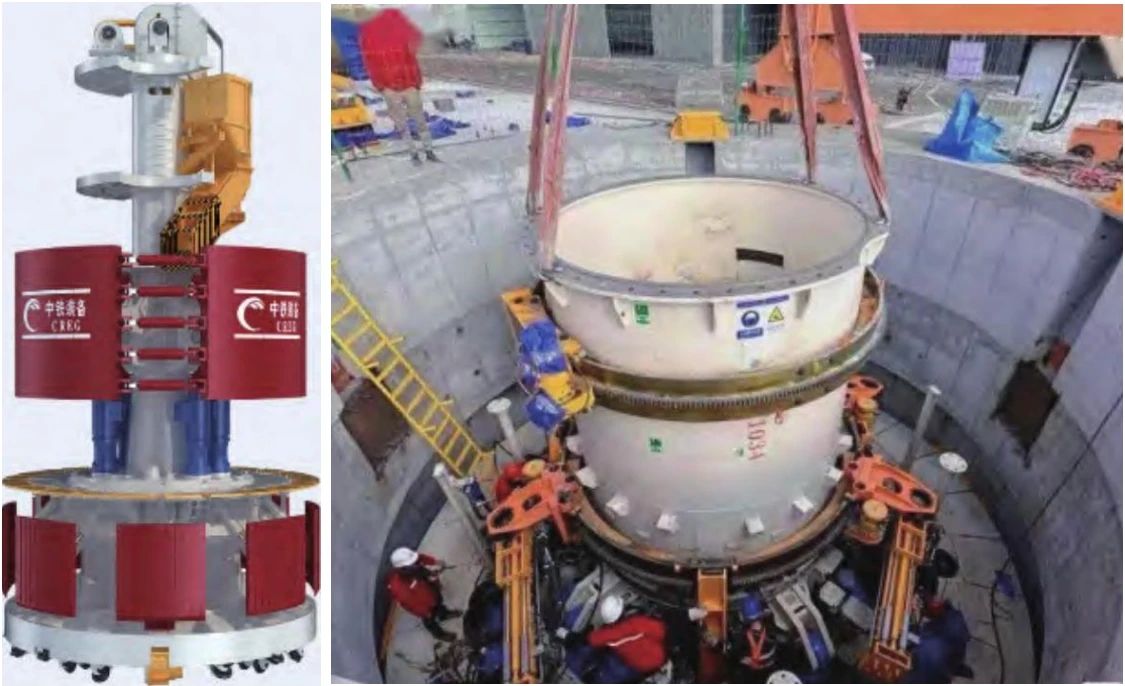
3、Proposed the design idea of slag discharge on shaft digging machine.
Put forward the working face → hoisting plate → ground three-stage slag discharge design form, through multi-stage slag discharge, to achieve slag discharge, digging masonry and well wall pouring part of the parallel operation, to build the shaft digging machine digging - support - transport synchronous operation mode, improve the construction efficiency. At the same time, it is also necessary to integrate the equipment, database, information feedback and other aspects to jointly promote the intelligent construction.

Publication 03
Journal : Cold Regions Science and Technology
Title: A model of segregation frost heave for saturated soil freezing under overburden pressure (2023)
Authors:Hanqing Chen, Xin Li*, Hao Xiong, Xiangsheng Chen, Dong Su
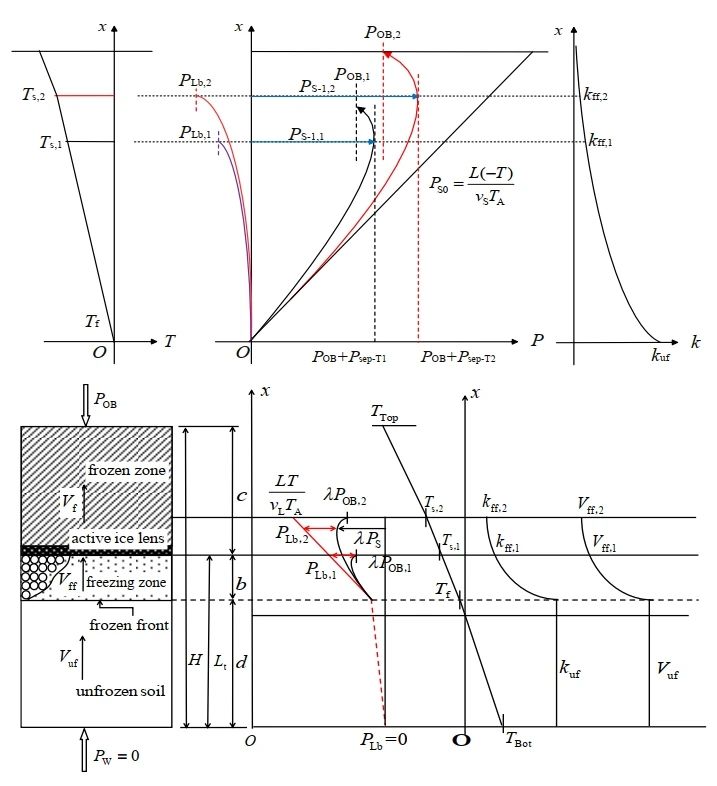
INTRODUCTION: Due to the multiphase and complexity of permafrost system, the analysis of freezing and thawing mechanism has always been a hot and difficult issue in the research of permafrost community. Especially, the inhibition mechanism of external pressure on frost heave has not been clarified, and the current research is still mainly based on numerical analysis, which lacks in-depth investigation on the theory of frost heave inhibition. In the study of the development and control mechanism of frost expansion, the analysis of the development mechanism of subcondensation ice formation is the key. To this end, we analyzed the distribution of pressure-absorption stress at the freezing edge by taking the growth and development of subcondensate ice at the end of the freezing edge as a breakthrough, and found that with the increase of external pressure and the difficulty of subcondensate ice formation, the subcondensate-freezing temperature decreases, and the permeability coefficient of the freezing edge decreases rapidly due to the blocking effect of the pore ice although the corresponding surface adsorption increases slightly, which has a strong inhibition effect on the migration of water. Accordingly, combined with Darcy's law, a model for the control of subconsolidation freezing and expansion of frozen soil under pressure was established, and the equation for the rate of water migration was given. This study not only improves the existing theory of freezing and expansion, but also has important significance in ensuring the construction safety of artificial freezing project and preventing freezing and expansion diseases.

Main innovation points:
1. A thin film water migration driving force model was constructed, giving the relationship between ice pressure, hydraulic pressure and interface pressure
Explained that the water migration driving force can be expressed either by hydraulic pressure difference or ice pressure difference, both of which represent the difference between the theoretical pressure in the equilibrium state and the actual pressure in the non-equilibrium state. When the actual ice pressure reaches the theoretical ice pressure, the pressure on both sides of the film water reaches equilibrium, at which time the moisture migration driving force decreases to zero and moisture migration stops.
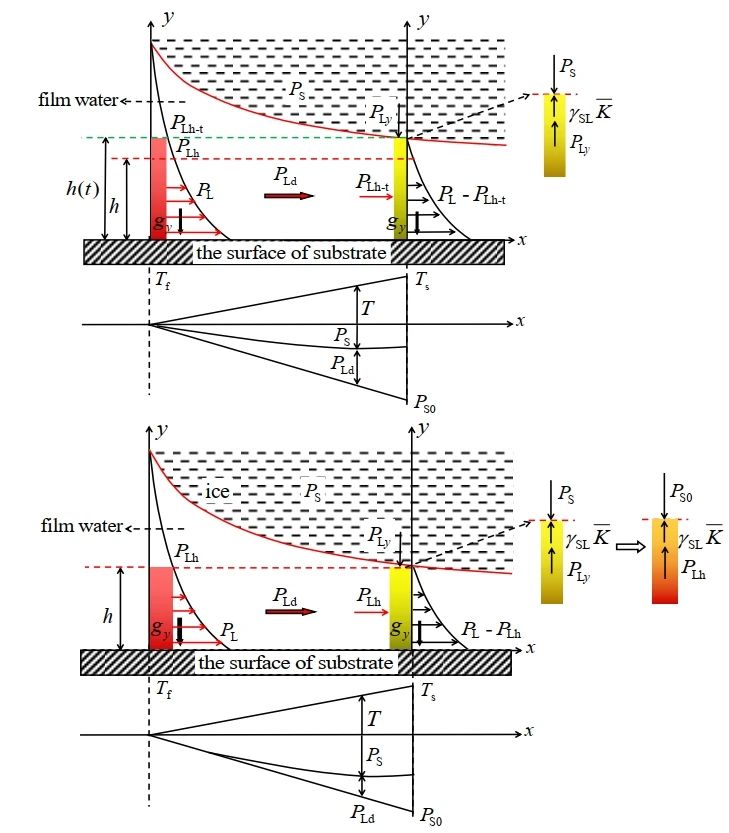
2. Constructed a pressure-suction stress transformation model, and revealed the conversion relationship between pressure variables and suction variables.
Explained that ice pressure can not only separate soil particles and form sub-condensate ice, but also offset and balance the theoretical suction (absolute suction), and under the joint action of ice pressure and theoretical suction, produce surface adsorption force (relative suction) that drives water migration. Of course, the combined effect of ice pressure and theoretical suction can not be simply expressed by mathematical addition or subtraction, there is a pressure and suction stress conversion factor λ between the two, and λ = -1.09.
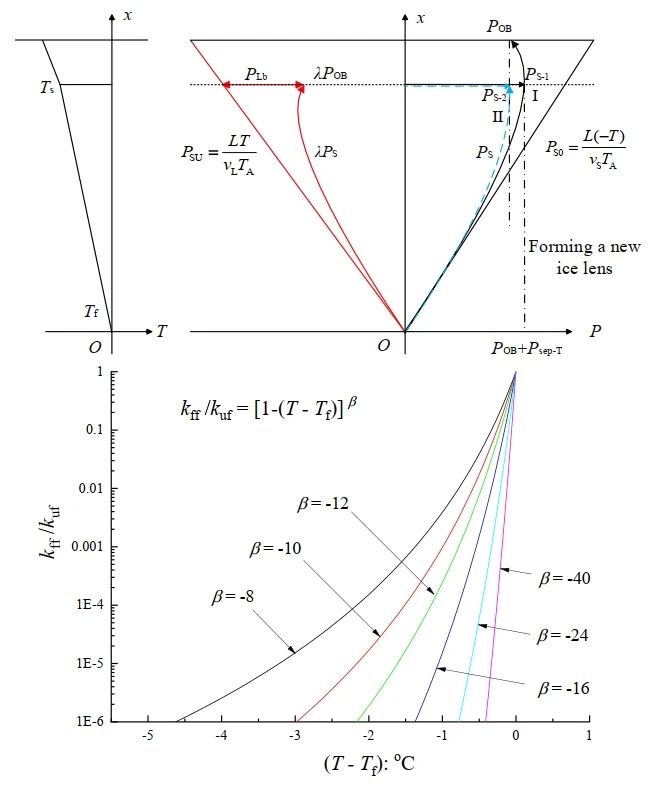
3. A subconsolidation freezing and expansion control model was constructed, revealing the inhibition mechanism of external pressure on water migration
The frozen soil is divided into three regions: frozen zone, positive frozen zone and unfrozen soil. Among them, the freezing edge, which has the greatest influence on the moisture migration rate, is located in the positive freezing zone. With the increase of external pressure, the subconsolidation-freezing temperature gradually decreased, resulting in a small increase of surface adsorption; however, the total permeability coefficient of the freezing edge decreased faster due to the blocking effect of pore ice, which ultimately resulted in a significant reduction of the water migration rate and the development of freezing and swelling was strongly inhibited.